Classification Models
Overview
The classification model shows each labeled class as a separate color per pixel. Each selection in the training data should consist only of the spectral bands that correspond to the pure classes. The model then predicts which class a pixel belongs to.
Use Case
Classify one or more materials / surfaces in an image.
Example
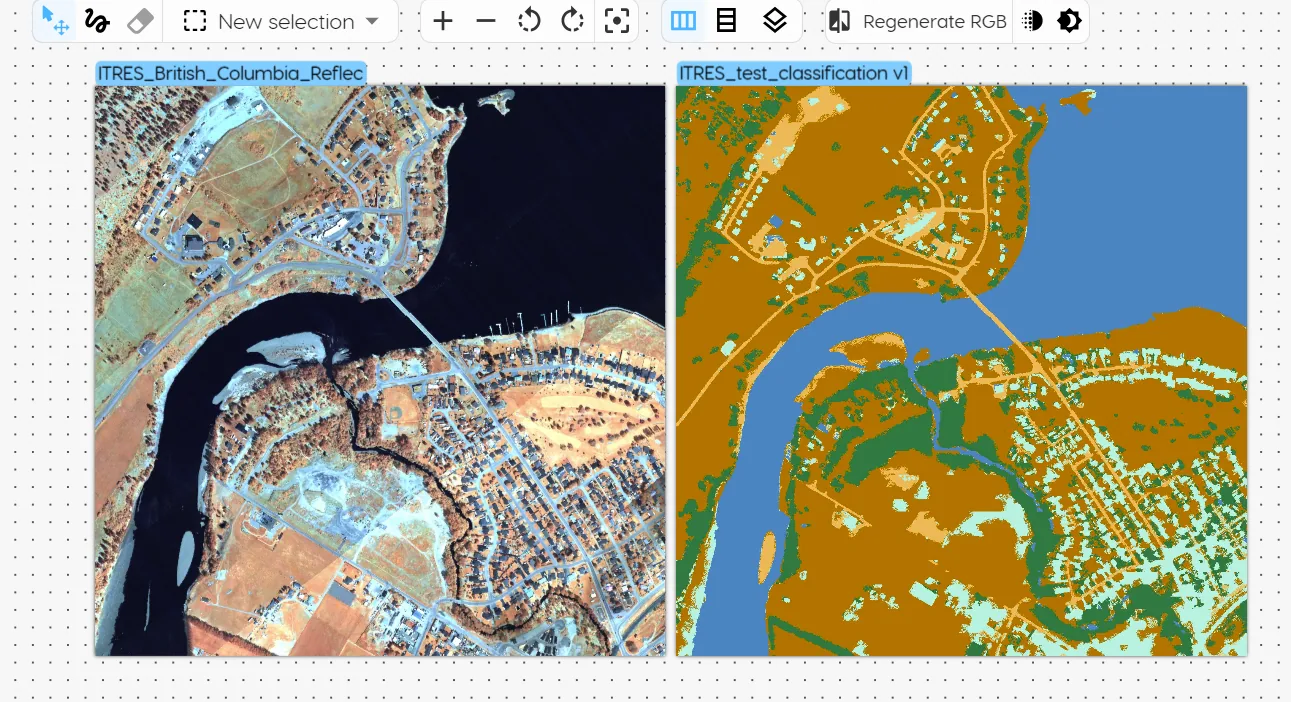
How It Works
Classification models analyze the spectral information contained within an image to assign each pixel to a specific class or category based on its spectral signature. They recognize patterns and distinctions in the data, enabling them to differentiate between various materials, vegetation types, water bodies, or man-made objects with high accuracy.
The result is a categorized map of the scene, where each pixel is labelled according to the type of material or object it represents, facilitating detailed analysis and monitoring of the earth's surface and its resources.
Strengths
- Highly effective at categorizing each pixel into predefined classes based on spectral signatures
- Ideal for creating detailed maps of land use, vegetation types, or other categorical data
- Excellent for scenarios where you need to map or monitor the distribution of specific types of materials, objects, or land cover across a scene